Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Food Vacuoles in Cellular Function
- Anatomy of Food Vacuoles: Exploring Their Structure and Composition
- How Food Vacuoles Contribute to Nutrient Absorption and Digestion
- Comparing Food Vacuole Activity in Different Organisms
- Enhancing Cellular Health Through Optimized Vacuole Function
- Q&A
- In Summary


Understanding the Role of Food Vacuoles in Cellular Function
At the heart of many eukaryotic cells, these tiny yet powerful structures are crucial to maintaining cellular health and activity. Acting much like the digestive system of a multicellular organism, they engulf large particles such as nutrients, sugars, and bacteria. Within their enclosed membrane, a series of enzymes break down these substances into smaller, usable components, providing cells the nutrients required for energy production, growth, and repair. Without their efficient processing and distribution network, cellular activities would grind to a halt.
Beyond their role in digestion, food vacuoles contribute significantly to homeostasis within the cellular environment. By sequestering harmful byproducts and isolating them, these structures protect the rest of the cell from potential damage. They also play a part in regulating osmotic pressure, ensuring that the balance of water and solutes remains steady, which is essential for cell turgor and stability. Through these multifaceted functions, they act not only as a feeding system but as a protective buffer safeguarding cellular integrity.
| Function | Role in Cell |
|---|---|
| Digestion | Enzyme Breakdown of Nutrients |
| Homeostasis | Regulation of Osmotic Pressure |
| Protection | Isolation of Harmful Substances |
Their adaptability and multifunctionality also showcase their evolutionary significance. By allowing cells to manage complex environments, food vacuoles enable single-celled organisms to thrive in a vast array of conditions, ranging from nutrient-rich waters to more hostile habitats devoid of readily accessible resources. This versatility highlights their role in evolutionary success, forming a bridge between primitive and more advanced cellular forms. Through these dynamic capabilities, they underscore the complexity and ingenuity inherent within even the simplest of life forms.

Anatomy of Food Vacuoles: Exploring Their Structure and Composition
At the heart of a cell’s digestive mechanism lies the food vacuole, a complex organelle pivotal to cellular sustenance. Activated through the endocytosis process, food vacuoles serve as transient storage units where internal and external components converge for degradation. Encased within a flexible membrane, these micro-ovens ensure that enzymes, particularly hydrolases, have a protected environment to break down nutrients. The membrane itself is uniquely structured, with selective permeability allowing particular ions and small molecules to traverse its boundary, ensuring effective digestive efficacy. The vacuole’s composition is dynamic, morphing as it encounters different substances to digest.
Inside, the milieu of the food vacuole is a sophisticated cocktail designed for optimal enzymatic action. Key components include:
- Hydrolytic enzymes
- pH regulators to maintain an acidic environment
- Receptors aiding in the selection of consumable particles
For a clearer understanding, consider the following constructs frequently visible in food vacuole contents:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Proteins | Broken down to release amino acids |
| Polysaccharides | Decomposed into simple sugars |
| Lipids | Converted to fatty acids and glycerol |
In essence, food vacuoles are miniature biochemical factories, optimizing the cellular intake process and transforming raw nutrients into energy and structural components vital for survival. Such intricate anatomy and composition underscore their significance in sustaining the microscopic world.


How Food Vacuoles Contribute to Nutrient Absorption and Digestion
The microscopic world within a cell unfolds intriguing mechanisms of how organisms manage their sustenance, with one key player being the food vacuole. Food vacuoles are pivotal cellular organelles that specialize in encasing ingested food items. This enveloping action isn’t just about storage; it’s an essential first step in breaking down nutrients. Enzymes are delivered to vacuoles, providing a controlled environment where nutrients are systematically dismantled into absorbable components. This enzymatic reaction is akin to an internal digestive tract for unicellular organisms, demonstrating a streamlined model of absorption that mirrors the complexities of multicellular beings.
| Process Step | Function |
|---|---|
| Enclosure by Vacuole | Protection and Isolation of Nutrients |
| Enzymatic Infusion | Initiation of Nutrient Breakdown |
| Absorption of Molecules | Integration into Cellular System |
Inside these vacuoles, the nutrient transformation process occurs in a series of highly coordinated steps. Once nutrient molecules break down into their simplest forms, they pass through the vacuole membrane into the surrounding cytoplasm where they’re utilized as building blocks or energy sources. A fascinating aspect of this process involves the vacuole’s selective permeability, which safeguards against the loss of vital cellular constituents while permitting the inward flow of beneficial substances. Through this intricate balance, cells ensure that nutrient absorption is efficient, catering precisely to their metabolic needs.
Effectiveness of the vacuole system lies not solely in nutrient absorption but also in its contribution to waste management. Post-digestive remnants that are non-absorbable accumulate within the vacuole before being transported to the cell membrane for expulsion. This waste clearance function highlights how food vacuoles engage in housekeeping roles that parallel complex bodily systems, thus maintaining cellular health. By efficiently managing both intake and expulsion within the cell, food vacuoles exemplify a time-tested model of cellular efficiency and adaptability.
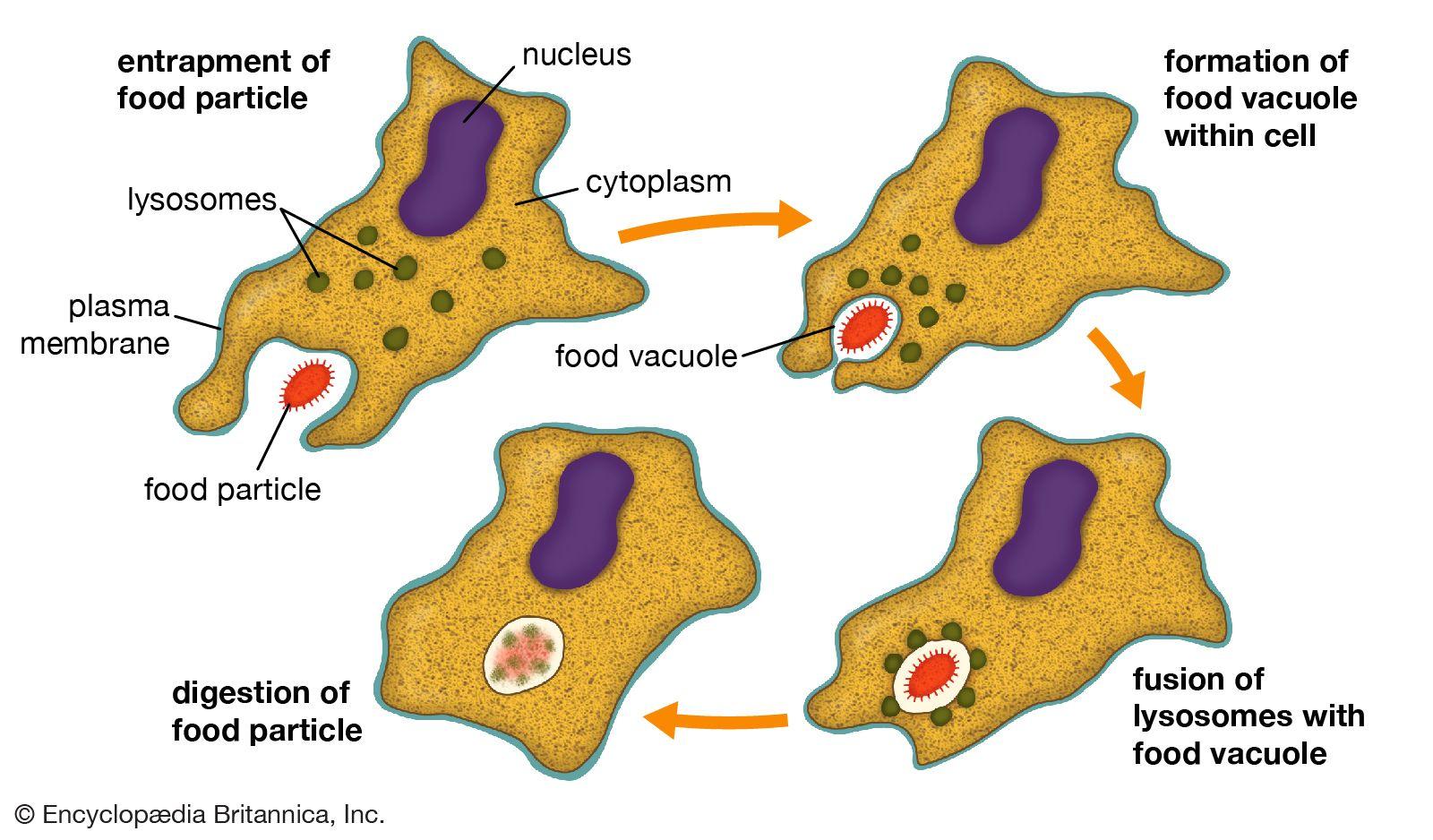

Comparing Food Vacuole Activity in Different Organisms
In the intricate web of life, food vacuoles serve as biological kitchens where complex digestion unfolds within unicellular organisms. Their function varies significantly across the microscopic world, illustrating a spectrum of survival strategies. For instance, in protozoans such as Amoeba, food vacuoles develop after phagocytosis, encompassing prey like bacteria. Here, enzymes are secreted into the vacuoles to break down the engulfed material, highlighting a process that is both reactive and adaptive. This contrasts with ciliates such as Paramecium, which utilize a more organized method where food is directionally swept into a gullet before being ensconced within a vacuole. Notably, in ciliates, the formation and transport of food vacuoles follow a more structured path, showcasing a well-orchestrated digestive ballet.
- Protozoan Variability: Diverse methods of prey capture and digestion.
- Amoeboid Simplicity: Engulfment followed by internal digestion.
- Ciliate Complexity: Precise entry to vacuoles post-cilliary action.
Exploring further into the fungal kingdom presents another dimension of food vacuole diversity. Fungi, unlike protozoans, predominantly rely on external digestion through hyphal seeping of enzymes, yet species like Cryptococcus exhibit unique food vacuole mechanics when conditions necessitate. Moreover, the slime molds present an intermediate scenario where large vacuoles form during their motile stages. These vacuoles act as temporary hubs for storing food that will be consumed later during the stationary phase. The comparison between fungi and slime molds highlights a captivating interplay between environmental constraints and cellular adaptations, emphasizing evolutionary ingenuity.
| Organism Type | Vacuole Role | Vacuole Formation |
|---|---|---|
| Protozoans | Digestive Encapsulation | Post-Phagocytosis/Structured Entry |
| Fungi | Storage and Conditional Digestion | Occasional, When Contained |
| Slime Molds | Storage and Deferred Use | During Motility |
Diving into a more niche corner of biology, certain algal species exhibit food vacuole traits similar to those seen in some plant-like protists. In environments where sunlight is scarce, such algae form food vacuoles to digest organic material and sustain their growth. This capability is indicative of the multifaceted roles vacuoles can assume depending on ecosystem demands and phylogenetic heritage. This adaptability in algae underscores a strategic confluence of autotrophy and heterotrophy, where food vacuoles become pivotal players in nutrient cycling. As one can discern, examining food vacuole activity across various organisms reveals a profound ecological tapestry illustrating nature’s resourcefulness in nutritional acquisition and efficiency.

Enhancing Cellular Health Through Optimized Vacuole Function
Optimizing the function of vacuoles is crucial for maintaining cellular health, given their role in nutrient storage and waste management. Vacuoles, often described as the cellular equivalent of a storage unit, are responsible for holding materials that the cell needs to survive. They help in sequestering harmful materials, holding valuable proteins, and maintaining proper pressure within the cell. One might wonder, how can we enhance the functionality of these cellular components? Incorporating a diet rich in antioxidants, essential minerals, and hydrating foods can significantly impact vacuole performance. Antioxidants from blueberries, green tea, and dark chocolate can mitigate cellular oxidative stress, thereby preserving the integrity and function of vacuoles.
Nutritional improvements are not the only way to support these organelles. Lifestyle factors, such as regular physical activity and adequate sleep, also play a vital role. Exercise promotes efficient nutrient absorption and waste elimination, indirectly supporting vacuolar efficiency. Moreover, a well-rested body can better regulate hormones and cellular processes, enhancing the potential of vacuoles to manage resources within cells effectively. Thus, adopting holistic habits can synergize with dietary changes to optimize cellular operations.
Understanding the importance of a balanced environment within cells highlights the need for regular health habits. Let’s explore some actionable steps you can take:
- Eat a Rich Variety of Foods: Incorporate leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains to bolster nutrient reserves.
- Stay Hydrated: Ensure sufficient water intake to maintain cellular turgor pressure necessary for vacuolar function.
- Regular Movement: Engage in activities such as walking, yoga, or cycling to enhance cellular efficiency.
By understanding these methods, you can contribute significantly to cellular health and the optimization of vacuole function, thus paving the path to increased vitality and well-being.




0 Comments